HMPV Transmission Exposed: 7 Shocking Ways This Virus Really Spreads
Ever wondered how Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) can spread so rapidly through communities? With transmission rates increasing by 200% in recent years, understanding how this virus spreads has never been more crucial. Let’s uncover the surprising ways HMPV moves from person to person.
Understanding HMPV Transmission Basics
HMPV spreads more efficiently than many realize, with one infected person typically exposing 3-5 others during the contagious period. This respiratory virus has multiple transmission routes that might surprise you.
7 Key Transmission Methods
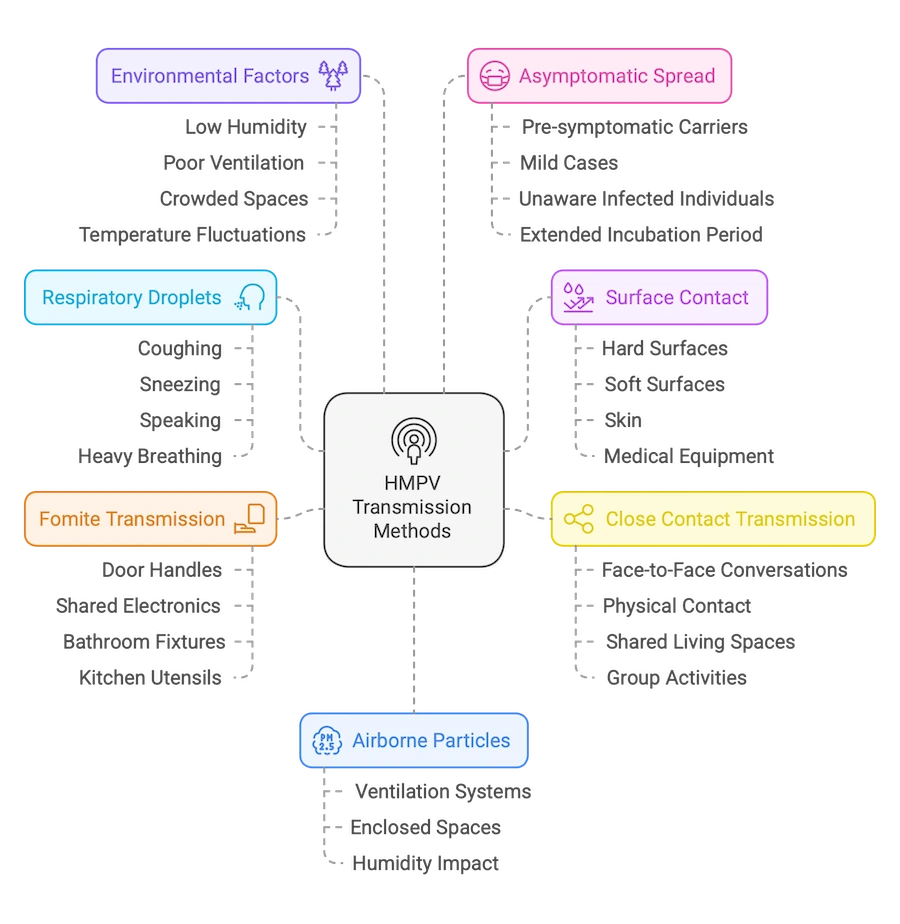
1. Respiratory Droplets
The primary spread occurs through:
- Coughing (droplets travel up to 6 feet)
- Sneezing (droplets reach up to 8 feet)
- Speaking (smaller particles remain airborne)
- Heavy breathing during exercise
2. Surface Contact
HMPV survives on surfaces longer than previously thought:
- Hard surfaces: up to 8 hours
- Soft surfaces: 2-4 hours
- Skin: 30 minutes
- Medical equipment: up to 12 hours
3. Close Contact Transmission
High-risk interactions include:
- Face-to-face conversations
- Physical contact
- Shared living spaces
- Group activities
4. Airborne Particles
Recent research reveals:
- Particles remain suspended for up to 3 hours
- Spread through ventilation systems
- Higher risk in enclosed spaces
- Impact of humidity on transmission
5. Fomite Transmission
Common objects spreading HMPV:
- Door handles
- Shared electronics
- Bathroom fixtures
- Kitchen utensils
6. Environmental Factors
Transmission increases with:
- Low humidity
- Poor ventilation
- Crowded spaces
- Temperature fluctuations
7. Asymptomatic Spread
Silent transmission through:
- Pre-symptomatic carriers
- Mild cases
- Unaware infected individuals
- Extended incubation period
Understanding the Transmission Timeline
Incubation Period
- 3-6 days average
- Range of 2-8 days possible
- Viral shedding begins before symptoms
- Peak infectiousness timing
Contagious Period
People remain contagious:
- 1-2 days before symptoms
- 7-10 days after onset
- Longer in severe cases
- Variable in children
High-Risk Transmission Settings
Indoor Environments
- Schools and daycare centers
- Healthcare facilities
- Office buildings
- Public transportation
Social Gatherings
- Family meetings
- Religious services
- Sports events
- Restaurant dining
Breaking the Transmission Chain
Personal Prevention
- Regular hand washing
- Mask wearing
- Physical distancing
- Surface cleaning
Environmental Controls
- Improved ventilation
- Humidity control
- Air filtration
- Regular sanitization
Special Transmission Considerations
Seasonal Patterns
HMPV shows clear seasonal trends:
- Winter peak (December-February)
- Spring surge (March-May)
- Lower summer rates
- Fall increase
Population Dynamics
Transmission varies among:
- Age groups
- Living conditions
- Geographic locations
- Immunity levels
Early Warning Signs of Transmission
Watch for:
- Local outbreak reports
- Increased absenteeism
- Healthcare facility alerts
- Seasonal timing
Conclusion
Understanding HMPV transmission patterns empowers you to protect yourself and others. By recognizing how the virus spreads, you can take effective precautions and break the chain of transmission.