HMPV Testing Revealed: 5 Powerful Methods You Need to Know Now

Wondering if you need an HMPV test? With respiratory infections on the rise, understanding your testing options for Human Metapneumovirus has never been more crucial. Let’s dive into the most effective testing methods that could give you the answers you need.
Why HMPV Testing Matters
Human Metapneumovirus affects millions globally each year, with testing accuracy reaching up to 95% when performed correctly. Early detection can significantly impact treatment outcomes, making it essential to understand your testing options.
The 5 Most Reliable HMPV Testing Methods
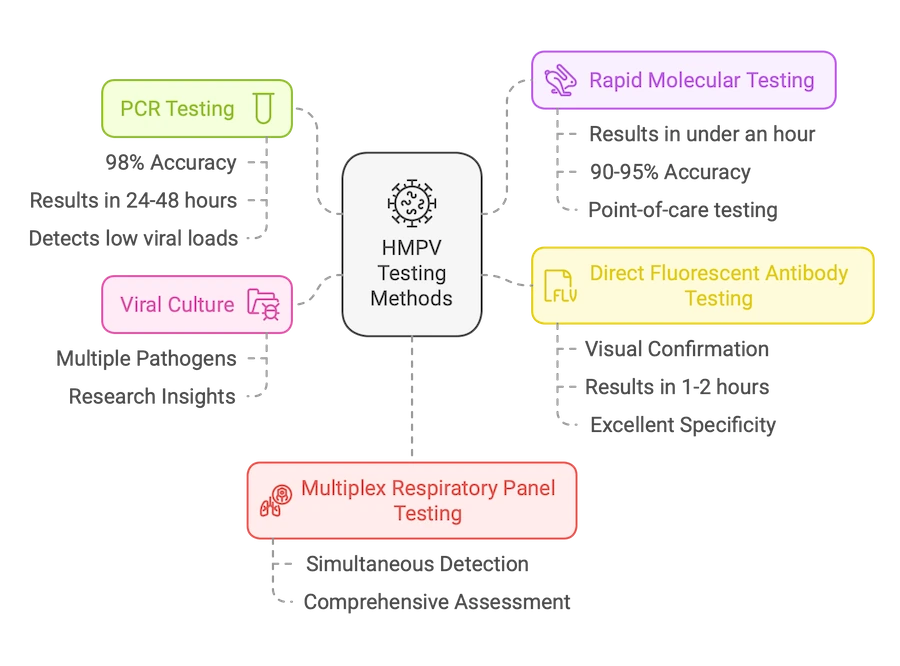
1. PCR Testing: The Gold Standard
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing leads the pack with:
- 98% accuracy rate
- Results within 24-48 hours
- Ability to detect even low viral loads
- Minimal false positives
2. Rapid Molecular Testing
Perfect for urgent situations, offering:
- Results in under an hour
- 90-95% accuracy
- Convenient point-of-care testing
- Reduced waiting time for treatment decisions
3. Direct Fluorescent Antibody Testing (DFA)
This method provides:
- Visual confirmation of viral presence
- Results within 1-2 hours
- Excellent specificity rates
- Cost-effective screening option
4. Viral Culture
Though slower, viral culture offers:
- Comprehensive viral analysis
- Ability to detect multiple pathogens
- Valuable research insights
- Definitive results
5. Multiplex Respiratory Panel Testing
Increasingly popular due to:
- Detection of multiple viruses simultaneously
- Comprehensive respiratory assessment
- Efficient diagnosis process
- Cost-effective for multiple pathogen testing
When Should You Get Tested?
Consider HMPV testing if you experience:
- Persistent cough
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever lasting more than 3 days
- Exposure to confirmed cases
- Belonging to high-risk groups
The Testing Process Explained
Sample Collection Methods
- Nasopharyngeal swabs
- Nasal aspirates
- Throat swabs
- Sputum samples
What to Expect During Testing
- Medical history review
- Sample collection (takes 1-2 minutes)
- Laboratory processing
- Results notification
Understanding Your Test Results
Positive Results
A positive test means:
- Active HMPV infection
- Need for isolation
- Treatment plan development
- Follow-up care scheduling
Negative Results
Negative results indicate:
- No current HMPV infection
- Possible need for additional testing
- Consideration of other causes
- Continued monitoring if symptoms persist
Special Considerations
Testing for High-Risk Groups
- Children under 5
- Adults over 65
- Immunocompromised individuals
- Healthcare workers
Cost and Insurance
Most insurance plans cover HMPV testing when:
- Ordered by a healthcare provider
- Medically necessary
- Performed at approved facilities
Latest Advances in HMPV Testing
Recent developments include:
- At-home testing options
- Faster processing times
- Improved accuracy rates
- Combined COVID-19 and HMPV testing
Making the Right Testing Choice
Consider these factors:
- Symptom severity
- Result turnaround time needs
- Cost considerations
- Healthcare provider recommendations
Conclusion
HMPV testing has evolved significantly, offering multiple reliable options for diagnosis. Choose the method that best fits your situation, and always consult with healthcare providers for guidance on the most appropriate testing approach.